What is force? Force is a form of energy, a push or pull applied to an object as a result of its interaction with another object.
Engineers calculate the external forces acting on a structure. They use this data to compute the corresponding internal stresses. From this, each piece of the structure is made to handle the forces/load without breaking.
There are some main forces/loads that can act on a structure. These include tension, compression, shear, and torsion. The strength of objects is measured using these forces. This helps product designers in producing the best products.
Tensile Strength
What is Tensile Force?
Tensile force acts on both opposite ends of an object by stretching or pulling.

How is Tensile Strength Calculated?
Tensile Strength is the highest load that a material can support without breaking when stretched. Engineers calculate it in the following way. They measure the highest load that a material can support without breaking when stretched. Then divide this by the material's original cross-sectional area to determine its tensile strength. This property is also sometimes referred to as Ultimate Tensile Stress or UTS.
Tensile Force in Hardware
A turnbuckle is tensioned from both ends to carry out its function. It must maintain an acceptable amount of tension force based on its maximum capability.

Examples of hardware are Rope Tensioners, Hold Down Latches, and Retractable Tie Downs.
Compressive Strength
What is Compression Force?
Compression force occurs when two pushing forces meet each other from the opposite direction.
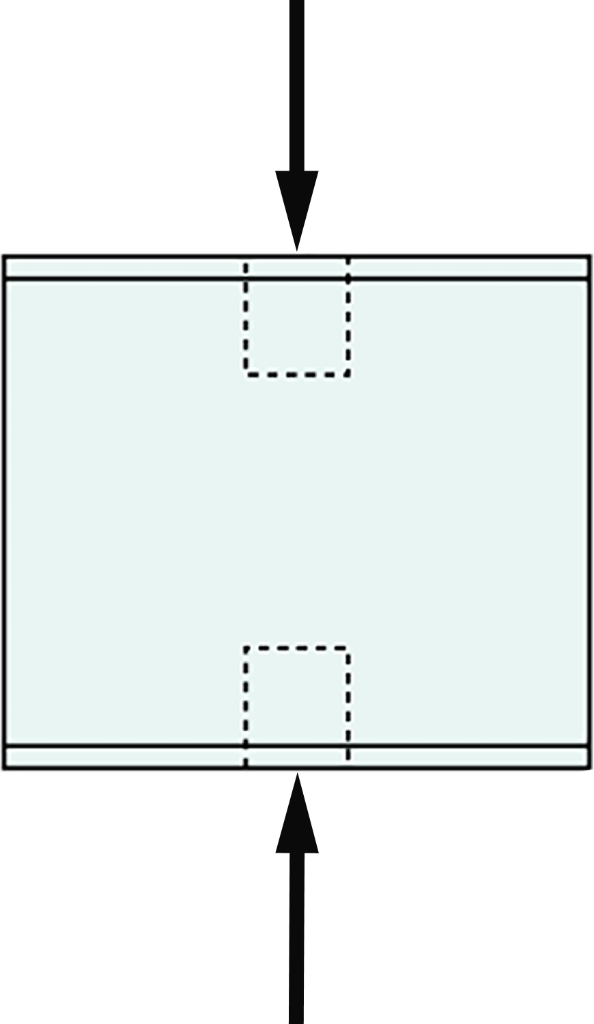
How is Compressive Strength Calculated?
Compressive strength is the greatest compressive stress that a solid material or structure can withstand without cracking under a progressively applied force.
Compression Force in Hardware
Anti-vibration mounts, often placed under engines, receive compression load from the engine. The weight of the engine compresses it down into the frame below.
Shear Strength
What is Shear Force?
Shear force occurs when two unaligned forces are pushing or pulling each other.
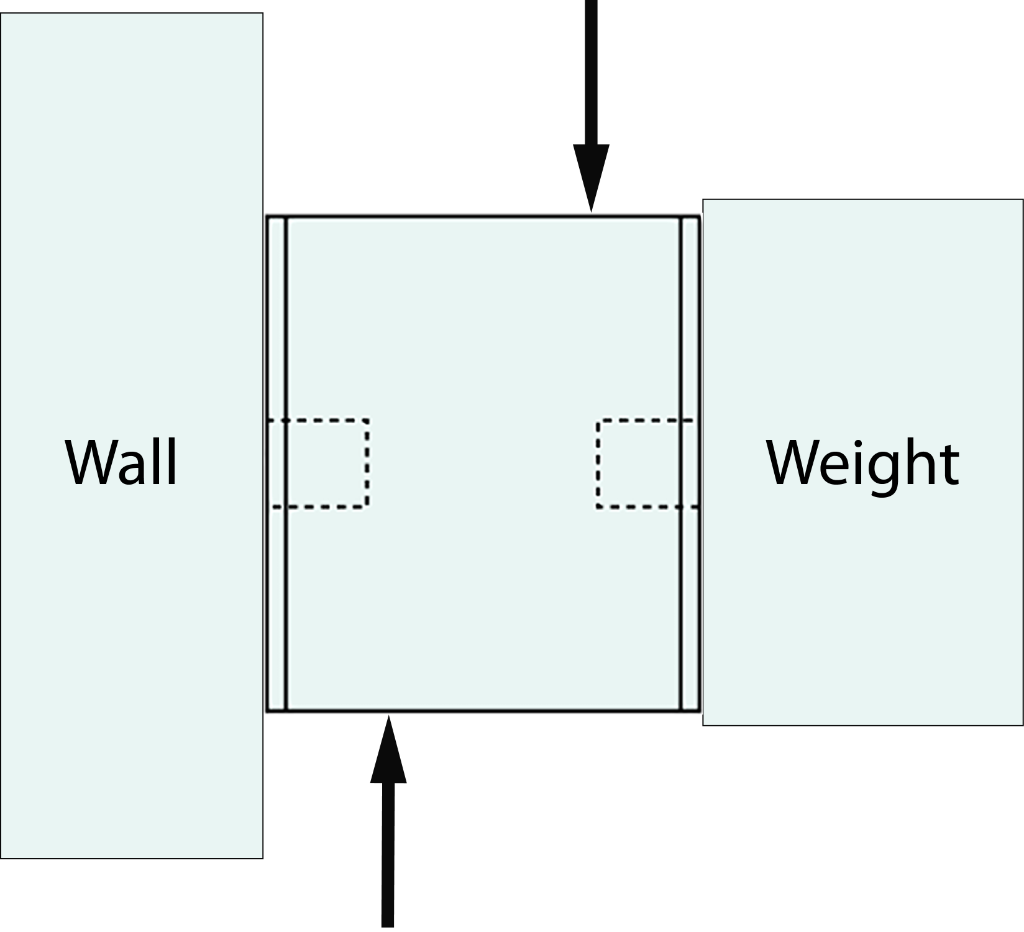
What is Shear Strength?
Shear strength is the ability of an object to resist the Shear Force. An object's shear strength can be measured in both vertical and horizontal directions.
Shear Strength in Hardware
An example of Shear Load is when an Anti-Vibration Mount is mounted sideways. The weight is pulling it down while the bolt is holding up. Other examples can be seen in adhesives applications.
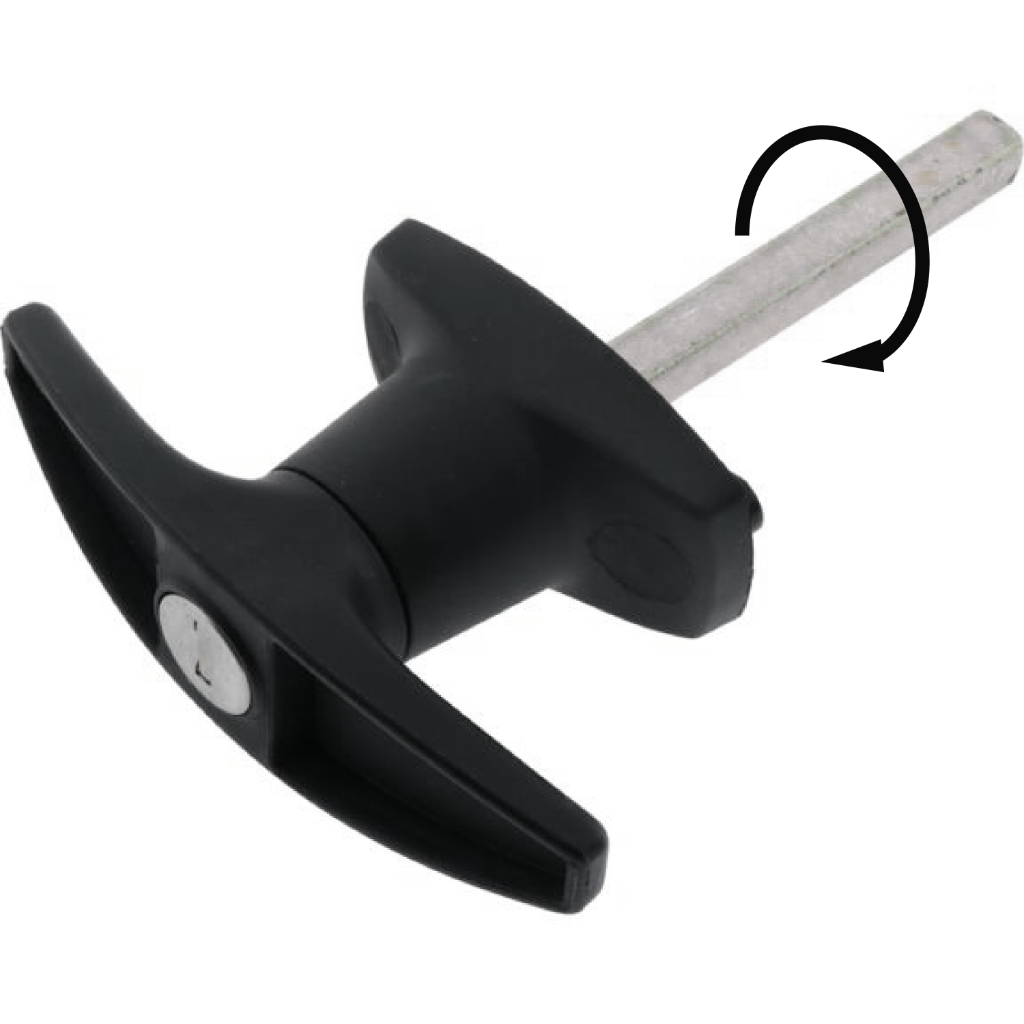
Torsional Force
What is Torsional Force?
Torsion force is a twisting or torque acting on an object. This causes one end or section of the object to rotate around a longitudinal axis. The other is kept still or rotated in the opposite direction.
What is Torsional Strength?
Torsional strength is the maximum amount of rotational force divided by the cross-sectional area that an object can endure before twisting off. This sort of force is commonly used in mechanical devices on spinning shafts.
A torsion test measures the amount of force applied in torsion. as well as the degrees of rotation that have happened. This measurement determines the amount of torsion force an object can withstand.
Torsional Force in Hardware
An example of torsion force is twisting the handle of a T handle. This puts torsional force on the 8mm shaft that is attached to a latch bar.





